Ball Screws
What is a Ball Screw?
Ball screws are low-friction and highly accurate mechanical tools that change rotational motion into linear motion. A ball screw assembly consists of a screw and nut with matching grooves that allow precision balls to roll between the two. A tunnel then connects each end of the nut allowing the balls to recirculate as needed.
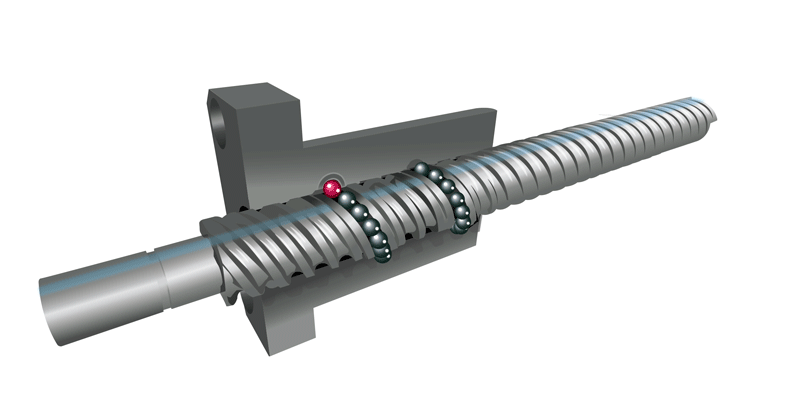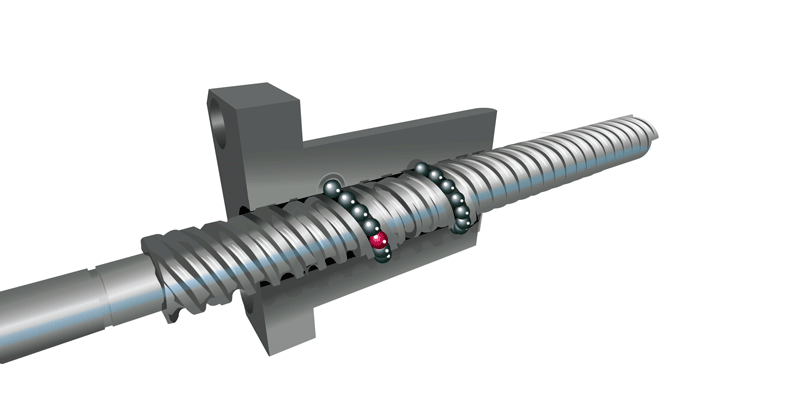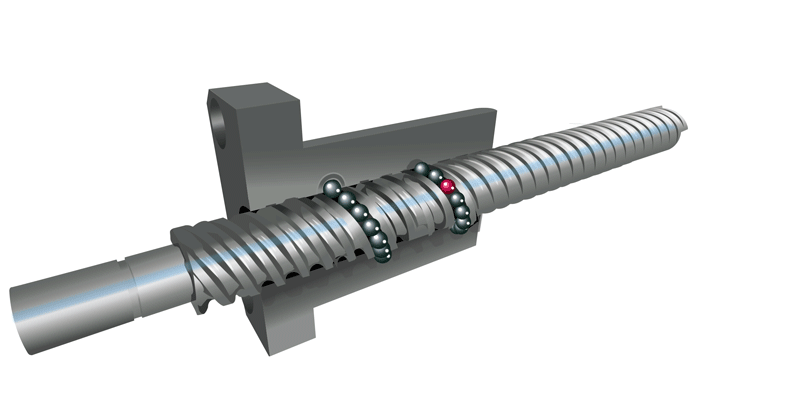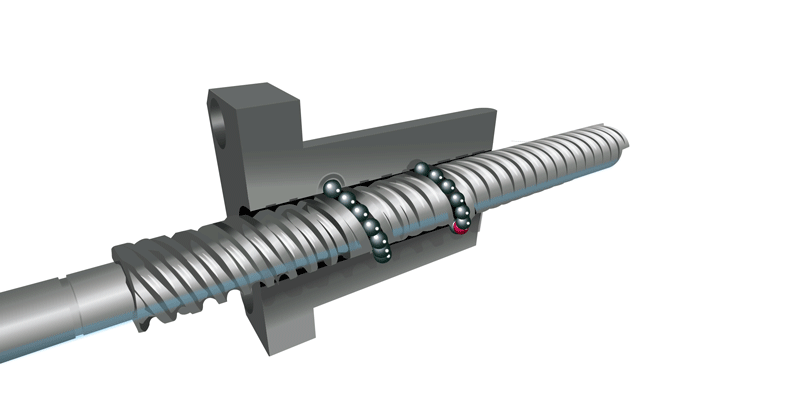
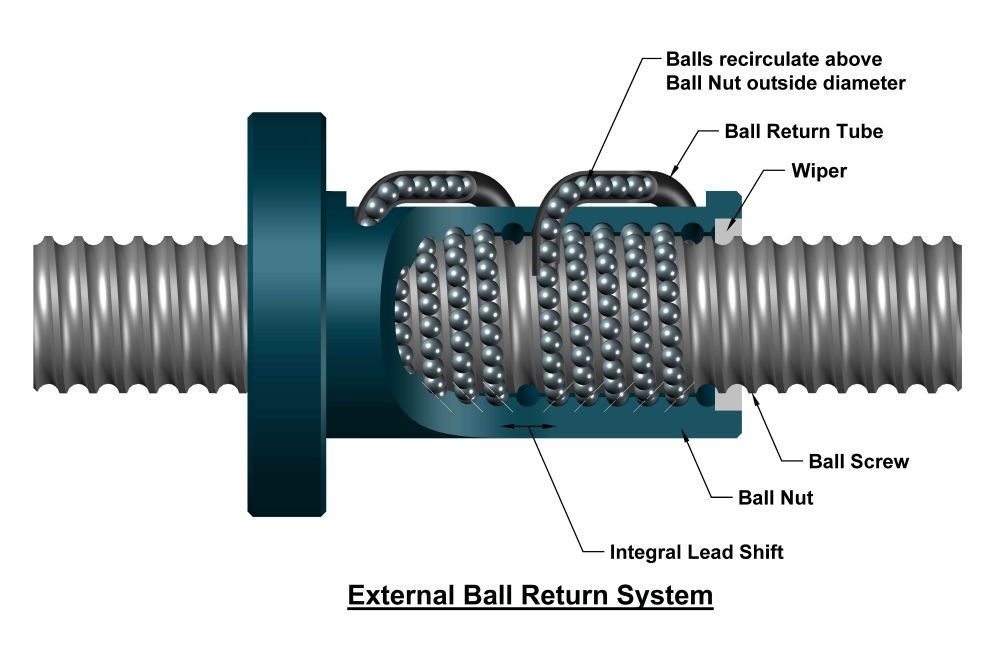
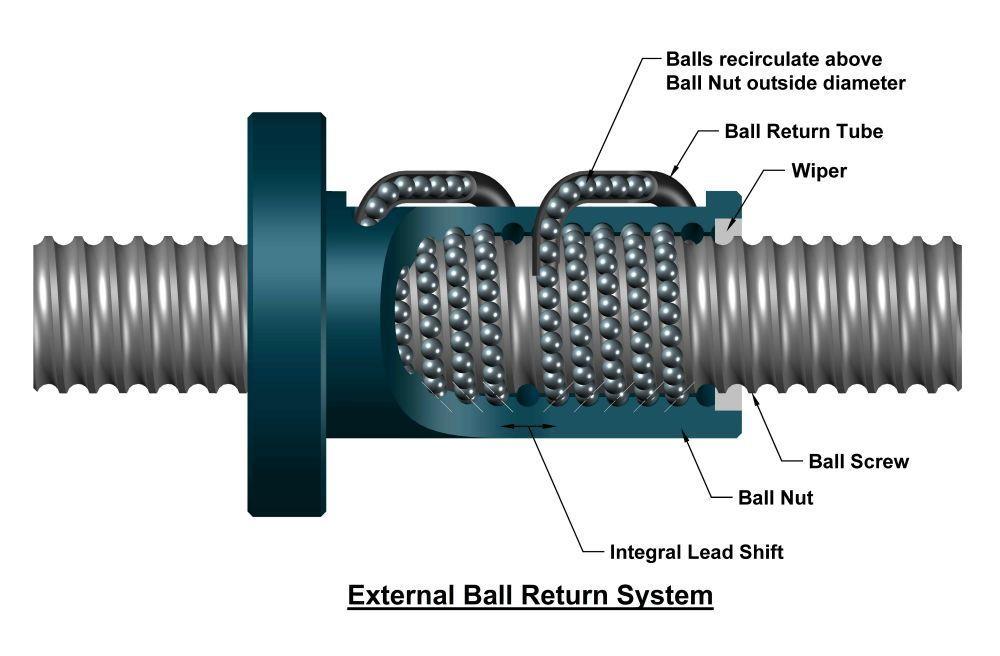
What is the Ball Return System?
The ball recirculating/return system is key to the ball screw design because, without it, all the balls would fall out when they reached the end of the nut. The ball return system is designed to recirculate the balls through the nut to continually feed them into the grooves while the nut moves along the screw. Weaker materials, such as plastic, may be used for the ball return path as the returning balls are not under significant loads.
Ball Screw Advantages
The main advantage of a ball screw over a typical lead screw and nut is the lower friction. Precision balls roll between the screw and nut as opposed to the sliding motion of the leadscrew nut. Less friction translates to a lot of advantages such as higher efficiency, less heat generation, and longer life expectancy.
- Higher efficiency allows for less power loss from the motion system as well as the option to use a smaller motor for generating the same thrust.
- Reduced friction by the ball screw design will create less heat, which can be critical in temperature-sensitive applications or high vacuum environments.
- Ball screw assemblies tend to last longer than typical leadscrew nut designs thanks to the low-friction design of stainless steel balls as opposed to sliding plastic material.
Ball screws can reduce or eliminate backlash which is common in lead screw and nut combinations. By preloading the balls to reduce the wiggle room between the screw and the balls, the backlash is vastly reduced. This is highly desirable in motion control systems where the load on the screw will change direction quickly. The stainless steel balls used in a ball screw are stronger than the threads used in a typical plastic nut, allowing them to handle a higher load. This is why ball screws are typically found in high-load applications like machine tools, robotics, and more.
Ball Screw Application Examples
- Medical Equipment
- Food processing Equipment
- Laboratory Equipment
- Automobile Power Steering
- Hydro Electric Station Water Gates
- Microscope Stages
- Robotics, AGV, AMR
- Precision Assembly Equipment
- Machine Tools
- Weld Guns
- Injection Molding Equipment